Birth Deformity
Bat Ear Deformity
Bat ear deformity, also known as prominent ear or protruding ear, is a congenital condition where the ears stick out more than usual from the sides of the head. This condition typically occurs due to an underdevelopment or malformation of the ear cartilage during fetal development. The defect can occur in latter stages also, due mishap or injury. Overly large ears are due to a rare condition called Macrotia whereas protruding ears occur on one or both sides in varying degrees.
While bat ear deformity does not affect hearing or physical health, it can have a significant psychological impact, especially on children. Individuals with prominent ears may experience self-consciousness, teasing, or bullying, which can lead to issues with self-esteem and social interaction.
Dr. Sushil Nahar, an expert in corrective ear surgery, understands the impact that bat ear deformity can have on a person's self-esteem. He specializes in otoplasty, designed to reshape the ear's cartilage, bringing the ears closer to the head and creating a more balanced appearance.
Treatment for bat ear deformity is typically surgical and is known as otoplasty or ear pinning surgery. This procedure involves reshaping or repositioning the ear cartilage to create a more natural appearance, closer to the head. Otoplasty is commonly performed on children between the ages of 5 and 7, as the ears are nearly fully developed by this age, but the surgery can also be performed on adults. The results of otoplasty are generally permanent, providing a lasting solution to the aesthetic concerns associated with bat ear deformity.
While bat ear deformity does not affect hearing or physical health, it can have a significant psychological impact, especially on children. Individuals with prominent ears may experience self-consciousness, teasing, or bullying, which can lead to issues with self-esteem and social interaction.
Dr. Sushil Nahar, an expert in corrective ear surgery, understands the impact that bat ear deformity can have on a person's self-esteem. He specializes in otoplasty, designed to reshape the ear's cartilage, bringing the ears closer to the head and creating a more balanced appearance.
Treatment for bat ear deformity is typically surgical and is known as otoplasty or ear pinning surgery. This procedure involves reshaping or repositioning the ear cartilage to create a more natural appearance, closer to the head. Otoplasty is commonly performed on children between the ages of 5 and 7, as the ears are nearly fully developed by this age, but the surgery can also be performed on adults. The results of otoplasty are generally permanent, providing a lasting solution to the aesthetic concerns associated with bat ear deformity.
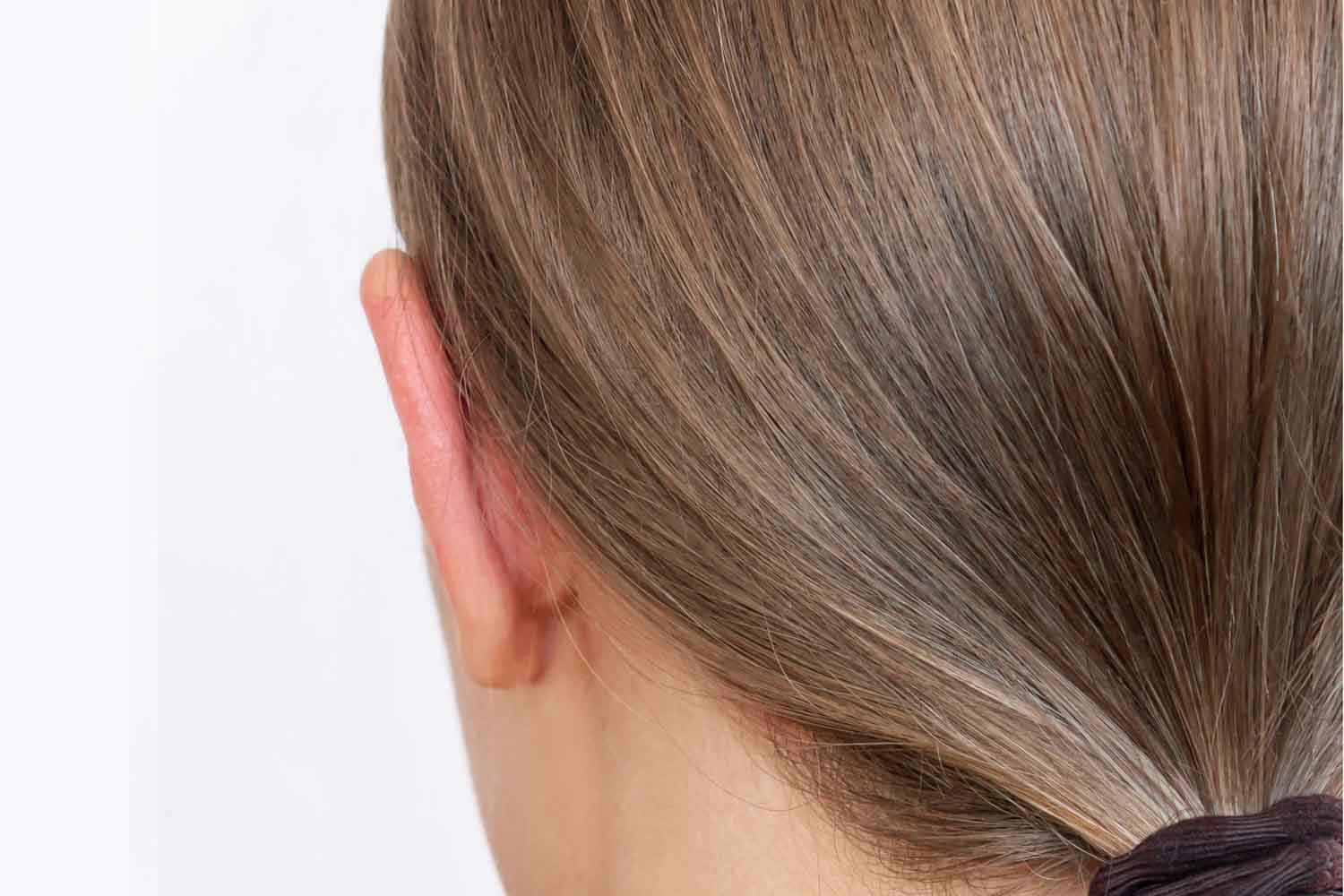 After
After  Before
Before Drag
Birth Deformity
Bat Ear Deformity Surgery Helps in
- The surgery reshapes and repositions the ears closer to the head, reducing the prominence and creating a more natural look.
- By adjusting the ear's position and shape, the procedure contributes to overall facial balance and harmony.
- Correcting the appearance of bat ear deformity can improve self-esteem, especially in children and adolescents who may face teasing or bullying.
- The surgery can help alleviate any social anxiety or discomfort associated with the appearance of prominent ears.
- The procedure can be tailored to address specific concerns, whether it’s reducing the size of the conchal bowl or creating a more defined antihelical fold.
our expert answers
frequently asked questions
Who is a good candidate for bat ear deformity surgery?
Good candidates include children as young as 5-7 years old, whose ears are fully developed, as well as adults who are self-conscious about their prominent ears and in good general health.
What can I expect during the surgery?
The surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia for adults and general anesthesia for children. It involves making small incisions behind the ear, reshaping or removing excess cartilage, and repositioning the ear closer to the head.
How long does the recovery take?
Recovery usually takes about 1-2 weeks. Most patients can return to normal activities within a week, though it’s recommended to avoid strenuous activities for several weeks.
Are the results of otoplasty permanent?
Yes, the results of otoplasty are generally permanent, providing long-lasting correction to the ear’s appearance.
Will there be visible scars after surgery?
The incisions are usually made behind the ear, so any scars are well-hidden and typically fade over time, becoming barely noticeable.
Is the surgery covered by insurance?
Otoplasty is generally considered a cosmetic procedure and is not covered by insurance unless it is performed to correct a congenital deformity or injury. It’s best to check with your insurance provider for specific coverage details.
APPOINTMENT
